Introduction
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), characterized by a decline in testosterone levels in aging men, has been a subject of increasing interest in the medical community. This condition not only affects the quality of life but also has potential implications for prostate health. In this article, we delve into the findings of a recent longitudinal study conducted on American men, which explores the relationship between LOH, PSA levels, and the risk of prostate cancer. This study provides crucial insights that could guide future clinical practices and patient counseling.
Understanding Late-onset Hypogonadism
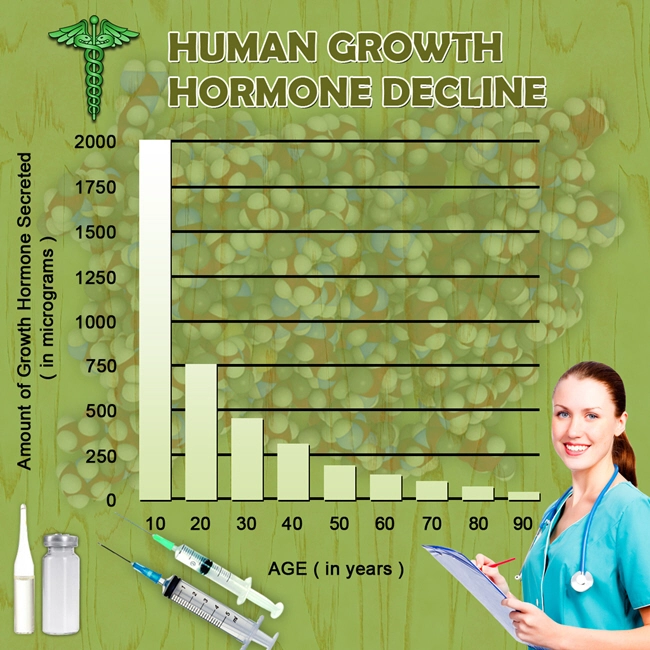
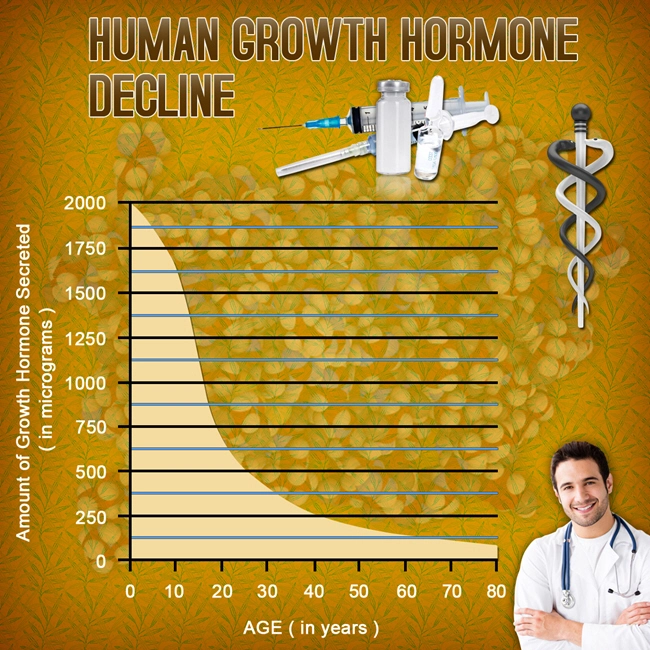
Late-onset hypogonadism is a clinical and biochemical syndrome associated with advancing age and characterized by symptoms and a deficiency in serum testosterone levels. Symptoms can include reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and mood disturbances. The prevalence of LOH increases with age, affecting a significant portion of the male population over 50.
Prostate Health and PSA Levels
Prostate health is a critical concern for aging men, with prostate cancer being one of the most common cancers among American males. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels are commonly used as a screening tool for prostate cancer. Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate issues, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer.
Study Design and Methodology
The longitudinal study involved a cohort of 1,200 American men aged 50 to 75 years, followed over a period of five years. Participants were assessed annually for testosterone levels, PSA levels, and other health parameters. The study aimed to determine whether LOH was associated with changes in PSA levels and an increased risk of prostate cancer.
Key Findings on PSA Levels and LOH
The study revealed a complex relationship between LOH and PSA levels. Men with lower testosterone levels were found to have higher PSA levels, suggesting a potential link between LOH and prostate health. However, this association was not linear; rather, it followed a U-shaped curve, indicating that both very low and very high testosterone levels could be associated with elevated PSA levels.
Prostate Cancer Risk and LOH
Regarding prostate cancer risk, the study found that men with LOH had a slightly increased risk of developing prostate cancer compared to those with normal testosterone levels. However, this risk was modulated by other factors such as age, family history, and lifestyle. The study emphasized the importance of considering these factors in the context of LOH and prostate health.
Implications for Clinical Practice
These findings have significant implications for clinical practice. Physicians should consider LOH as a potential factor when evaluating PSA levels and assessing prostate cancer risk. Routine screening for testosterone levels in men over 50 could help identify those at higher risk of prostate issues. Moreover, lifestyle interventions aimed at maintaining optimal testosterone levels might play a role in prostate health management.
Limitations and Future Directions
While the study provides valuable insights, it is not without limitations. The sample size, although substantial, may not fully represent the diversity of the American male population. Additionally, the study did not account for all potential confounding factors that could influence the relationship between LOH and prostate health. Future research should aim to address these limitations and further explore the mechanisms underlying the observed associations.
Conclusion
The longitudinal study on American men provides compelling evidence of a relationship between late-onset hypogonadism, PSA levels, and prostate cancer risk. These findings underscore the importance of considering LOH in the context of prostate health and highlight the need for integrated approaches to managing both conditions. As research continues to unravel the complexities of LOH and its impact on men's health, clinicians and patients alike can benefit from a more nuanced understanding of these interconnected health issues.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging U.S. Men: Challenges and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments and Future Directions for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Men Over 40: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Screening, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mood, Energy, and Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Vitality Maintenance [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Nutrition, Diet, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Holistic Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Long-term Effects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism on American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Life Quality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cognitive Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Independence for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Stress and Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Late-Onset Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Journey and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Careers and Workplace Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Men's Health and Intimate Relationships in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Education, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Risks and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Impacts and Financial Challenges for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cultural Impacts on American Men's Health and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Care in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Technological Advances in Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Vital Role of Family Support in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Diagnosis and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Vital Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Self-Esteem: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Peer Support and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Social Impacts and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress Reduction Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Advocacy's Role in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism Through Diet and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for American Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Exercise and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Support Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Professional Performance and Career [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Personalized Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Care for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Leveraging Community Resources for Holistic Care [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Therapists' Crucial Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Challenges, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]