Introduction
Alzheimer's disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, poses a significant challenge to cognitive health among American males. As the quest for effective interventions continues, the role of testosterone in cognitive function has garnered attention. This article delves into a neuropsychological study exploring the potential of the Androderm testosterone transdermal patch in enhancing cognitive abilities in this vulnerable population.
Understanding Alzheimer's Disease and Cognitive Decline
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to neuronal damage and cognitive impairment. American males affected by this condition often experience a decline in memory, attention, and executive functions, significantly impacting their quality of life. The search for therapeutic strategies to mitigate these effects is crucial.
The Role of Testosterone in Cognitive Health
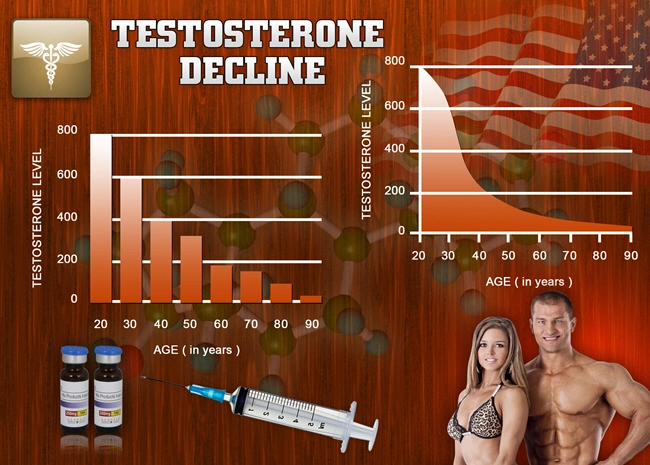
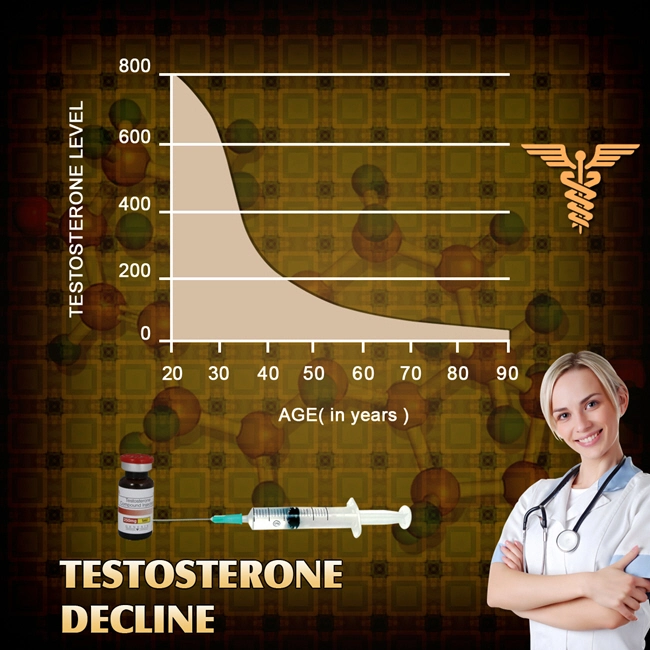
Testosterone, a hormone traditionally associated with male physiology, has been linked to various aspects of brain function. Research suggests that testosterone levels may influence cognitive performance, with lower levels correlating with increased risk of cognitive decline. This has led to investigations into testosterone replacement therapy as a potential intervention for cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease.
Androderm Testosterone Transdermal Patch: Mechanism and Application
The Androderm testosterone transdermal patch is a novel delivery system designed to provide a consistent supply of testosterone to the body. By adhering to the skin, the patch releases testosterone, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This method offers a controlled and sustained release, potentially optimizing the hormone's cognitive benefits.
Study Design and Methodology
The neuropsychological study focused on American males diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. Participants were divided into two groups: one receiving the Androderm patch and the other a placebo. Cognitive assessments were conducted at baseline and after six months of treatment, evaluating memory, attention, and executive function using standardized neuropsychological tests.
Results: Cognitive Improvements with Androderm
The study revealed promising results for the group using the Androderm patch. Participants showed significant improvements in memory recall and attention compared to the placebo group. Executive function, particularly task-switching and problem-solving, also demonstrated notable enhancements. These findings suggest that the Androderm patch may play a role in slowing cognitive decline in American males with Alzheimer's disease.
Potential Mechanisms of Action
The cognitive benefits observed may be attributed to testosterone's neuroprotective effects. Testosterone has been shown to promote neuronal survival, enhance synaptic plasticity, and reduce amyloid-beta accumulation. These mechanisms could contribute to the observed improvements in cognitive function among study participants using the Androderm patch.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The results of this study have significant implications for the management of Alzheimer's disease in American males. The Androderm testosterone transdermal patch could serve as a valuable adjunct to existing treatments, potentially improving quality of life for patients. However, further research is needed to confirm these findings and explore the long-term effects of testosterone therapy on cognitive health.
Considerations and Limitations
While the study provides encouraging evidence, several considerations must be addressed. The sample size was relatively small, and the study duration was limited to six months. Additionally, individual responses to testosterone therapy may vary, necessitating personalized approaches to treatment. Future studies should aim to include larger cohorts and longer follow-up periods to validate these findings.
Conclusion
The neuropsychological study on the Androderm testosterone transdermal patch offers a glimmer of hope for American males battling Alzheimer's disease. By demonstrating potential improvements in cognitive function, this research paves the way for further exploration of testosterone's role in neurodegenerative disorders. As we continue to unravel the complexities of Alzheimer's disease, interventions like the Androderm patch may prove to be valuable tools in the fight against cognitive decline.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- 0001) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Males with Low Levels [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- 0002) Androderm: Balancing Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks in Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0003) Androderm: Enhancing Life for American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0004) Androderm: Benefits for Hypogonadism vs. Prostate Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0005) Androderm: Enhancing Libido and Well-being in American Males with Testosterone Patches [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0006) Androderm: Convenient Transdermal Testosterone Patch for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0007) Androderm: Managing Side Effects and Optimizing Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0008) Androderm Patch: Boosting Energy in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0009) Androderm: Boosting Muscle Mass and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0010) Androderm: Enhancing American Male Health with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0011) Androderm: Combating Fatigue in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0012) Androderm Therapy: Restoring Vitality in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0013) Androderm: Enhancing Athletic Performance in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0014) Androderm: Effective Transdermal Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0015) Androderm: Innovative Transdermal Patch for Treating Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0016) Androderm: Enhancing American Male Health and Quality of Life with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0017) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0018) Androderm: Enhancing American Men's Health with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0019) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0020) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0021) Androderm: A Breakthrough in Testosterone Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0022) Androderm's Impact on Mood: Enhancing Mental Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0023) Androderm: Enhancing American Men's Health with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0024) Androderm: Effective Transdermal Testosterone Patch for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0025) Androderm: Effective Transdermal Testosterone Patch for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0026) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Replacement for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0027) Androderm: Effective Transdermal Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0028) Androderm: Testosterone Patch Effects on Male Fertility and Treatment Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0029) Androderm's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0030) Androderm: Enhancing Skin Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0031) Androderm: Enhancing Vitality in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0032) Androderm: Enhancing Male Wellness with Testosterone Patch Therapy in America [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0033) Androderm: Enhancing Life Quality in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0034) Androderm: Enhancing Physical and Mental Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0035) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Replacement for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0036) Androderm: Essential Monitoring for American Men's Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0037) Androderm: Effective Transdermal Testosterone Therapy for Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0038) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0039) Androderm: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0040) Androderm: Enhancing Life for American Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0041) Androderm: Maximizing Benefits for Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0042) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0043) Androderm: Enhancing Heart Health with Transdermal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0044) Androderm: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0045) Androderm: Enhancing Longevity and Quality of Life in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0046) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0047) Androderm: Effective Transdermal Testosterone Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0048) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0049) Androderm: Revolutionary Testosterone Patch for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0050) Androderm: Enhancing American Males' Vitality with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0051) Androderm: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- 0052) Androderm: Empowering American Men with Transdermal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- 0053) Androderm: A Comprehensive Guide to Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- 0054) Androderm: Boosting Energy in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- 0055) Androderm: Restoring Testosterone Levels in American Men for Enhanced Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- 0056) Androderm: Enhancing American Men's Health with Transdermal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0057) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0058) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Deficiency Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- 0059) Androderm: Optimizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- 0060) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0061) Androderm: Enhancing Physical Performance in American Men with Testosterone Patch [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0062) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Deficiency Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0063) Androderm: Enhancing Men's Health and Vitality with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0064) Androderm: Enhancing Cognitive and Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0065) Androderm: Enhancing Health and Vitality in American Men with Testosterone Patch [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0066) Androderm: Transdermal Testosterone Patch for Managing Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0067) Androderm: Innovative Testosterone Patch for American Males' Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0068) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0069) Androderm: Enhancing Heart and Sexual Health in Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0070) Androderm: Enhancing Male Health with Testosterone Patch Therapy in the US [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0071) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- 0072) Androderm: Revolutionizing Testosterone Deficiency Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- 0073) Androderm: Effective Testosterone Replacement for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0074) Androderm: Enhancing Physical, Mental, and Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0075) Androderm: Enhancing Sexual, Cardiovascular, and Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0076) Androderm: Revolutionizing Men's Health with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0077) Androderm Patch Safety: A Decade Review in American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- 0078) Androderm: Enhancing Men's Health and Wellness with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- 0079) Androderm Patch Shows Superior Bioavailability in TRT for American Males: Clinical Trial [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- 0080) Androderm: Enhancing Men's Health with Testosterone Patch Therapy [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]