Introduction
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), characterized by a decline in testosterone levels in aging males, has been increasingly recognized as a significant health concern. While its effects on sexual function and overall well-being are well-documented, emerging research suggests a potential association between LOH and liver health. This article explores the intricate relationship between late-onset hypogonadism and liver function, as well as its implications for liver disease risk among American males.
Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism
Late-onset hypogonadism, also known as age-related low testosterone or andropause, typically manifests in men over the age of 40. Symptoms may include reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood changes. While the primary focus has been on its impact on sexual health and quality of life, recent studies have begun to uncover its broader systemic effects, including potential links to metabolic and liver health.
The Liver's Role in Hormonal Regulation
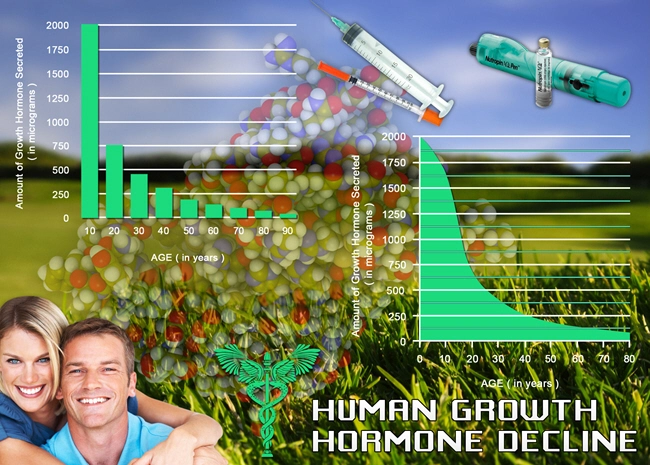
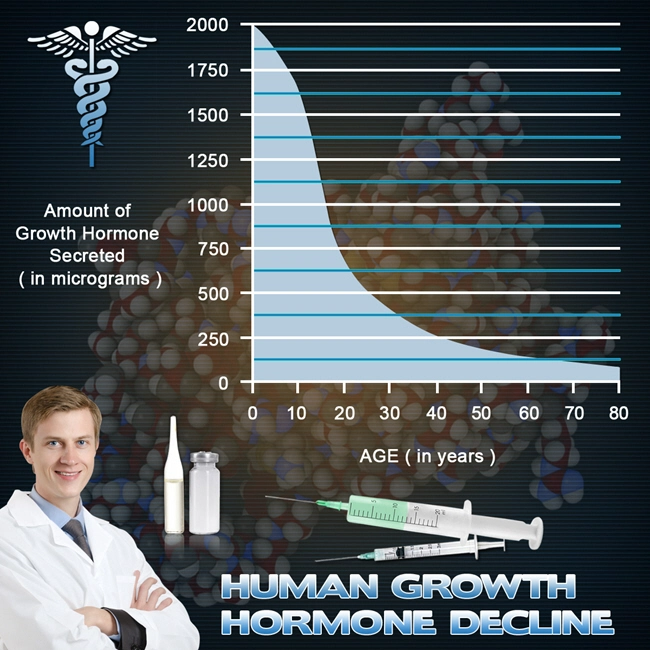
The liver plays a crucial role in the metabolism and regulation of hormones, including testosterone. It is responsible for converting testosterone into its active form and clearing excess hormones from the bloodstream. Any disruption in liver function can potentially affect hormone levels and vice versa, creating a complex interplay between the two systems.
LOH and Liver Function: The Emerging Evidence
Recent research has started to shed light on the relationship between late-onset hypogonadism and liver function. Studies have shown that men with LOH may exhibit altered liver enzyme levels, such as elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are indicators of liver stress or damage. These findings suggest that low testosterone levels could be associated with compromised liver function.
Impact on Liver Disease Risk
The potential link between LOH and liver health extends beyond mere enzyme alterations. Some studies have indicated that men with low testosterone levels may have an increased risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition characterized by fat accumulation in the liver that can progress to more severe liver diseases. The exact mechanisms behind this association are still being investigated, but it is hypothesized that testosterone may play a protective role against the development of NAFLD.
Implications for American Males
Given the high prevalence of both late-onset hypogonadism and liver disease among American males, understanding the potential connection between the two is of paramount importance. As the population ages, the incidence of LOH is expected to rise, which could have significant implications for liver health. Healthcare providers should be aware of this potential link and consider screening for liver function in men presenting with symptoms of LOH.
Managing LOH and Liver Health
For American males diagnosed with late-onset hypogonadism, a comprehensive approach to managing both their hormonal and liver health is essential. This may include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), lifestyle modifications such as weight management and regular exercise, and regular monitoring of liver function. It is crucial for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both conditions.
Future Research Directions
While the current evidence suggests a potential link between late-onset hypogonadism and liver health, more research is needed to fully understand the nature of this relationship and its implications for American males. Future studies should focus on elucidating the underlying mechanisms, determining the long-term effects of LOH on liver disease progression, and exploring the potential benefits of testosterone therapy on liver health.
Conclusion
The emerging evidence linking late-onset hypogonadism to liver health underscores the importance of a holistic approach to men's health. As American males age, it is crucial to consider the potential impact of declining testosterone levels on liver function and disease risk. By raising awareness of this connection and promoting further research, healthcare providers can better serve their male patients and help mitigate the burden of both LOH and liver disease in the population.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- 0001) Exploring Alternative Therapies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- 0002) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0003) Economic Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging U.S. Men: Challenges and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0004) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0005) Genetic Factors in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0006) Innovative Treatments and Future Directions for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0007) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Men Over 40: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0008) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0009) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Screening, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0010) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mood, Energy, and Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0011) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Vitality Maintenance [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0012) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0013) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Nutrition, Diet, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0014) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0015) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0016) Holistic Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0017) Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0018) Long-term Effects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism on American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0019) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0020) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Life Quality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0021) Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0022) Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0023) Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0024) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cognitive Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0025) Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0026) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0027) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Independence for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0028) Hormone Replacement Therapy: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0029) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0030) Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0031) Stress and Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0032) Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0033) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0034) Community Support Enhances Late-Onset Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0035) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Journey and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0036) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Careers and Workplace Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0037) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Men's Health and Intimate Relationships in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0038) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Education, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0039) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Risks and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0040) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0041) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Impacts and Financial Challenges for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0042) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0043) Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0044) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0045) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cultural Impacts on American Men's Health and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0046) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0047) Advocating for Better Care in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0048) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0049) Technological Advances in Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0050) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Vital Role of Family Support in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0051) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Diagnosis and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0052) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0053) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Vital Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0054) Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Self-Esteem: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- 0055) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Peer Support and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- 0056) Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- 0057) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Social Impacts and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- 0058) Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- 0059) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress Reduction Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0060) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Advocacy's Role in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0061) Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- 0062) Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism Through Diet and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0063) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for American Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0064) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0065) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0066) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0067) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Exercise and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0068) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Support Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0069) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Professional Performance and Career [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0070) Endocrinologists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0071) Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0072) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Personalized Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0073) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0074) Comprehensive Care for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0075) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0076) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0077) Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Leveraging Community Resources for Holistic Care [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0078) Therapists' Crucial Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0079) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Challenges, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- 0080) Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]