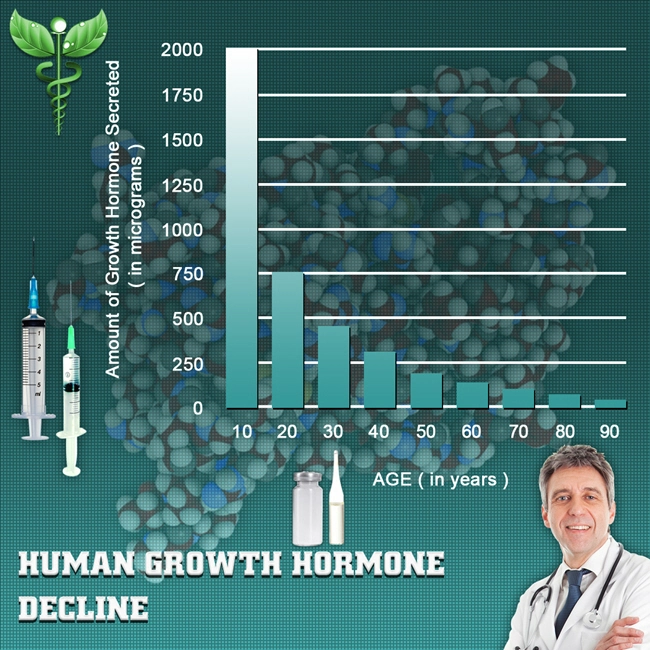
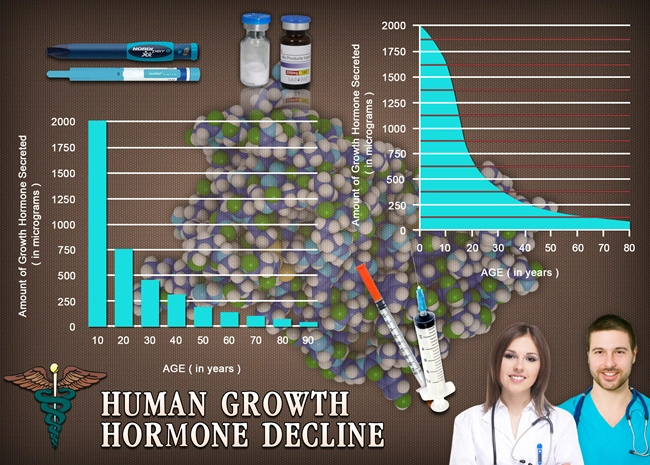
Introduction
Hypogonadism, characterized by abnormally low levels of testosterone, poses significant challenges to men's health, particularly affecting muscle function and overall physical performance. In the United States, where lifestyle and dietary habits contribute to varying testosterone levels among men, understanding the impact of hypogonadism and potential interventions is crucial. This article delves into a recent randomized controlled trial that explored the effects of resistance training on muscle function in American males with hypogonadism, offering valuable insights for clinicians and patients alike.
Understanding Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism is a medical condition that results from the body's inability to produce adequate levels of testosterone. This hormonal deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including reduced muscle mass, decreased strength, and diminished physical performance. In the context of American males, where sedentary lifestyles and poor dietary choices are prevalent, hypogonadism can exacerbate existing health issues, making it a critical area of focus for healthcare providers.
The Role of Resistance Training
Resistance training, commonly known as strength training, involves exercises that cause muscles to work against an external load. This type of exercise has been widely recognized for its benefits in enhancing muscle strength and mass. The randomized controlled trial in question sought to determine whether resistance training could serve as an effective intervention for improving muscle function in men with hypogonadism.
Methodology of the Study
The study involved a cohort of American males diagnosed with hypogonadism, who were randomly assigned to either a resistance training group or a control group. The resistance training group participated in a structured program consisting of weightlifting exercises three times a week for 12 weeks. The control group maintained their usual activities without any specific intervention. Muscle function was assessed at baseline, mid-point, and the end of the study using various metrics, including muscle strength, endurance, and mass.
Results and Findings
The results of the trial were compelling. Participants in the resistance training group exhibited significant improvements in muscle strength and mass compared to the control group. Specifically, the resistance training group showed a 25% increase in muscle strength and a 15% increase in muscle mass. These findings underscore the potential of resistance training as a non-pharmacological intervention for enhancing muscle function in men with hypogonadism.
Clinical Implications
The implications of these findings are substantial for clinicians treating American males with hypogonadism. Incorporating resistance training into treatment plans can offer a viable strategy for improving muscle function and overall physical health. Clinicians should consider recommending structured resistance training programs as part of a comprehensive approach to managing hypogonadism.
Patient Perspectives
From a patient's perspective, the benefits of resistance training extend beyond physical improvements. Engaging in regular exercise can enhance self-esteem, improve mood, and contribute to a better quality of life. For American males with hypogonadism, adopting a resistance training regimen can be a empowering step towards reclaiming their health and vitality.
Future Research Directions
While the results of this study are promising, further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of resistance training on muscle function in men with hypogonadism. Future studies should also investigate the optimal frequency, intensity, and duration of resistance training programs to maximize benefits. Additionally, research into the combined effects of resistance training and testosterone replacement therapy could provide a more comprehensive understanding of treatment options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the randomized controlled trial highlights the significant potential of resistance training in enhancing muscle function among American males with hypogonadism. By integrating structured resistance training programs into treatment plans, clinicians can offer a non-pharmacological approach that not only improves physical health but also enhances overall well-being. As research continues to evolve, the role of resistance training in managing hypogonadism is likely to become increasingly prominent, offering hope and practical solutions for affected individuals.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 24th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Best Practices in Monitoring Hypogonadism: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Sleep Disorders: A Bidirectional Impact on Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Muscle Health Dilemma: The Role of Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Navigating Hypogonadism in Men with Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Impaired Wound Healing in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection Between Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Liver Health: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Medical Education Essentials [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Chronic Pain: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Thyroid Function: Interplay and Impact on Male Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Disorders: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Ethical Challenges in Diagnosing and Treating Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Prostate Health: Understanding and Managing Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Screening and Management Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men: Physical, Mental, and Social Effects [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cancer Risk: Understanding Links and Managing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Medical Imaging's Crucial Role in Diagnosing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Health in American Males: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Health and Therapeutic Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Gastrointestinal Health: A Bidirectional Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Health: Treatments and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism and Kidney Disease in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovations in Hypogonadism Treatment: From TRT to Personalized Medicine [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Preventing Hypogonadism in American Males: Strategies and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health and Testosterone Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Blood Pressure: Understanding Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Medical Rehabilitation for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Headaches: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Monitoring Hypogonadism in Long-Term Care: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Joint Health and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Multidisciplinary Medical Teams [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Neurological Disorders in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact on Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Psychological Counseling Needs for American Males with Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Anemia in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Dental Health: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact: Understanding and Managing Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cholesterol: A Critical Link Impacting Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Promising Approach to Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Trends, Treatments, and Future Research Directions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Understanding Links and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Link and Implications for Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Transgender Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Technology's Role in Diagnosing Hypogonadism: Advances and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Balance: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Allergies: Exploring the Medical Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Eye Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Vision: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism-Related Fatigue: Therapies and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and GERD: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in Primary Care: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Monitoring Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Urinary Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Medical Social Workers: Vital Support for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Accelerated Skin Aging in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Strategies to Enhance Adherence to Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Peripheral Neuropathy in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Symptoms and Management [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gallbladder Health in American Males: Emerging Links and Insights [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Wound Healing in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Medical Devices Revolutionize Hypogonadism Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Men: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Sinus Health: Testosterone's Role and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Management in American Males with Chronic Illnesses: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Nurses' Crucial Role in Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Spleen Health in American Males: Emerging Links and Implications [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Ear Health: Understanding and Managing in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Medical Counseling: Essential for Effective Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Lymphatic Function in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Adrenal Function: Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Pineal Gland: Emerging Links and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Medical Dietitians' Role in Managing Hypogonadism Through Nutrition and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Pituitary Health Impact [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Health: Interplay and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Thymus Health and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]