Introduction
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has become a cornerstone in managing hypogonadism in American males, offering improvements in libido, muscle mass, and overall well-being. Among the various modalities of TRT, the Striant testosterone buccal system represents a unique approach by delivering testosterone via a buccal mucoadhesive tablet. Given the liver's pivotal role in metabolizing hormones, understanding the hepatic impact of such therapies is paramount. This article delves into a comprehensive two-year hepatological study aimed at elucidating the effects of the Striant system on liver function in American males.
Study Design and Methodology
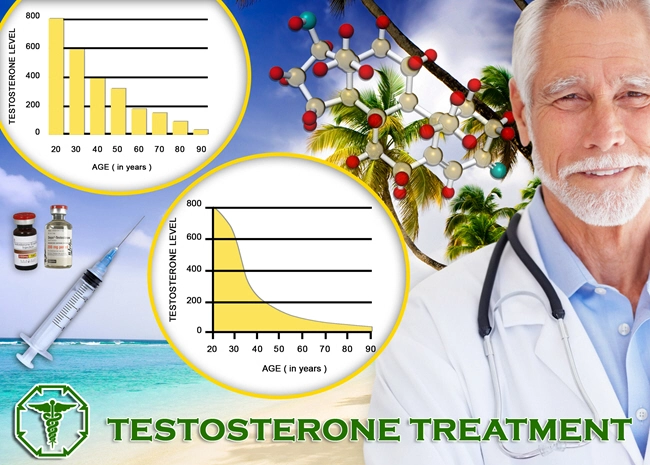
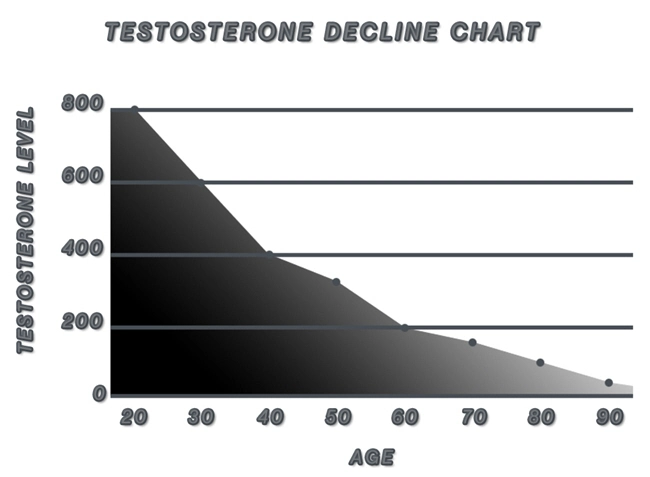
The study encompassed a cohort of 150 American males aged between 30 and 65 years, diagnosed with hypogonadism and prescribed the Striant testosterone buccal system. Participants underwent regular monitoring of liver function tests (LFTs), including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and bilirubin levels, at baseline and at six-month intervals over two years. The primary objective was to assess any alterations in these parameters that could indicate hepatic stress or dysfunction attributable to the buccal testosterone delivery.
Results: Liver Function Parameters
Over the two-year period, the study found no significant elevations in ALT, AST, ALP, or bilirubin levels among the participants. The mean values of these LFTs remained within the normal range throughout the study duration, suggesting that the Striant testosterone buccal system does not adversely affect liver function in American males with hypogonadism. This finding is crucial as it alleviates concerns regarding potential hepatotoxicity associated with testosterone therapy.
Discussion: Implications for Clinical Practice
The absence of significant changes in liver function parameters in this study supports the safety profile of the Striant testosterone buccal system from a hepatological standpoint. Clinicians can confidently prescribe this form of TRT to American males, knowing that it does not pose a risk to liver health. This is particularly reassuring given the historical concerns over oral testosterone formulations, which have been linked to liver toxicity.
Comparison with Other TRT Modalities
When juxtaposed with other TRT modalities, such as injectable or transdermal testosterone, the Striant system offers a non-invasive and convenient alternative without compromising liver safety. This is a significant advantage, as it expands the therapeutic options available to patients and healthcare providers, allowing for personalized treatment plans that cater to individual preferences and lifestyles.
Patient Perspectives and Quality of Life
Participants in the study reported high satisfaction with the Striant system, citing ease of use and minimal side effects. The maintenance of normal liver function further contributed to their overall quality of life, as it eliminated the need for additional monitoring or concerns about liver health. This aspect underscores the importance of considering patient-reported outcomes in the evaluation of TRT efficacy and safety.
Limitations and Future Research Directions
While the study provides robust evidence on the hepatic safety of the Striant testosterone buccal system, it is not without limitations. The sample size, although adequate, may not capture rare adverse events. Future research should aim to include larger cohorts and longer follow-up periods to further validate these findings. Additionally, exploring the long-term effects on other organ systems and overall metabolic health would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the Striant system's impact.
Conclusion
The two-year hepatological study on the Striant testosterone buccal system in American males with hypogonadism demonstrates that this form of TRT does not adversely affect liver function. This finding reinforces the safety and efficacy of the Striant system, offering clinicians and patients a reliable option for managing hypogonadism. As TRT continues to evolve, ongoing research and vigilance will be essential in ensuring the optimal health and well-being of American males undergoing testosterone replacement therapy.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Striant: Enhancing Vitality in Aging American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Striant: Managing Testosterone Deficiency and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Striant Buccal System: A Convenient Testosterone Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Striant: Advanced Buccal Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Striant: Buccal Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Striant: Innovative Buccal System Boosts Testosterone, Energy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Striant: A Convenient Buccal Solution for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Striant: Buccal Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism - Fertility and Reproductive Health Impacts [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Striant: Innovative Buccal Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Males with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Body Composition through Testosterone Therapy in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Striant: A Convenient TRT Solution for Young American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Striant: Innovative Buccal System for Testosterone Deficiency Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Striant: A Lifeline for American Men Battling Chronic Fatigue with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Striant: A Novel Buccal System for Enhancing Male Libido in Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Striant: A Promising Testosterone Therapy for Managing Metabolic Syndrome in Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Striant: Essential Monitoring for Effective Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Striant: Effective Buccal Testosterone Therapy for Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Striant Buccal System: Innovative TRT for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Striant: Effective Testosterone Replacement for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Life Post-Prostatectomy with Buccal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Striant: Advanced Buccal System for Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Joint Health and Mobility in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Striant: A Buccal Solution for Muscle Wasting in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Mental Health in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Mood and Cognitive Function in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Striant: A Non-Invasive Testosterone Therapy Option for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Striant: A Novel Approach to Managing Hair Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant's Role in Enhancing Cardiovascular Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Bone Health in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy with Buccal System for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Respiratory Health in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Health and Resilience Through Buccal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant TRT: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Health While Managing Oral Care [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Striant: A Novel Approach to Managing Obesity and Testosterone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Auditory Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Skin Health and Vitality in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Striant: Advancing Male Fertility with Buccal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Striant Buccal System: A Comprehensive Guide to Testosterone Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Kidney and Urinary Health via Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Digestive Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Eye Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Liver Health via Buccal Testosterone Delivery [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Striant: Advancing Hormonal Health with Buccal Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Striant: Revolutionizing Men's Skin Health Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Striant Buccal System: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Neurological Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Endurance and Stamina via Buccal Testosterone Delivery [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Health via Buccal Testosterone Delivery [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Cardiovascular Fitness and Heart Health [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Sexual Health and Well-being in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Bone Density in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Men's Metabolic Health and Energy via Buccal Testosterone Delivery [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Joint Flexibility and Managing Arthritis in Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Prostate Health and Cancer Prevention in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Vision Clarity and Eye Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Muscle Growth and Recovery via Buccal Testosterone Delivery [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Dental Health and Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Hair Growth in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Emotional Resilience and Reducing Stress in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Striant's Impact on Digestive Efficiency and Gut Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Liver Health and Detoxification in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Striant: A Buccal System Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Respiratory Health in American Men via Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Sleep and Circadian Rhythms in Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Reproductive Health in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Kidney Function and Urinary Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Male Vitality and Skin Health Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Hearing Acuity in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Striant: Enhancing Neurological Health and Cognitive Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Striant: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men with Buccal System [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Striant Buccal System: 15-Year Safety Review in American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Cost-Effectiveness of Striant Testosterone Buccal System Across Socioeconomic Groups [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
- Striant: Advancing Male Health with Buccal Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]