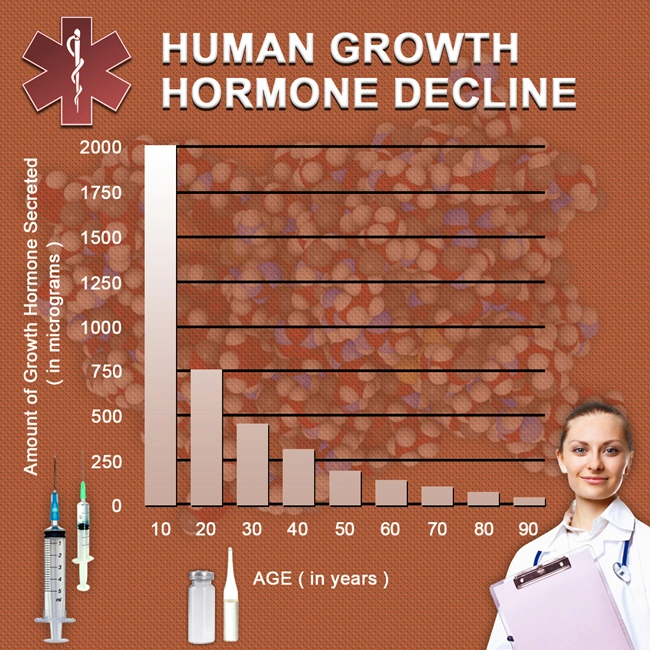
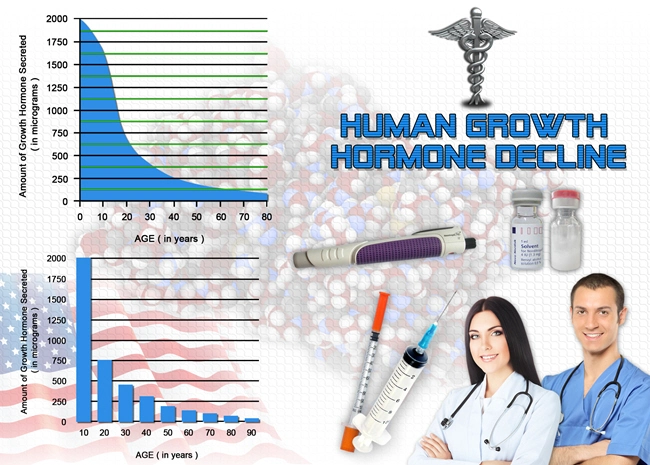
Introduction
Prostate health remains a critical concern for American males, with chronic inflammation emerging as a significant factor in the development of various prostate conditions. This article delves into the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying chronic inflammation in the prostate and reviews the current therapeutic interventions aimed at mitigating its effects. Understanding these aspects is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and prevent prostate-related diseases.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Chronic Prostate Inflammation
Chronic inflammation within the prostate gland is a complex process involving multiple cellular and molecular pathways. The initiation of inflammation often stems from infections, hormonal imbalances, or autoimmune responses. Once triggered, the inflammatory response can lead to the infiltration of immune cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes into the prostate tissue. These cells release cytokines and chemokines, which perpetuate the inflammatory state and can lead to tissue damage and remodeling.
One of the key mechanisms in chronic prostate inflammation is the activation of the NF-?B pathway. This pathway is central to the regulation of immune response and inflammation, and its persistent activation can lead to the development of prostatic diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. Additionally, oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species and antioxidants, further exacerbates the inflammatory environment, contributing to cellular damage and disease progression.
Impact of Chronic Inflammation on Prostate Health
Chronic inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several prostate conditions prevalent among American males. For instance, chronic prostatitis, a common condition characterized by persistent pelvic pain, is often associated with ongoing inflammation. Similarly, BPH, which affects a significant proportion of aging males, is linked to inflammatory processes that contribute to the enlargement of the prostate gland.
Moreover, the role of chronic inflammation in prostate cancer is increasingly recognized. Inflammation can promote a microenvironment conducive to malignant transformation and tumor growth. Studies have shown that men with higher levels of inflammatory markers in their prostate tissue have an increased risk of developing aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
Therapeutic Interventions for Chronic Prostate Inflammation
Addressing chronic inflammation in the prostate requires a multifaceted approach. Current therapeutic strategies focus on reducing inflammation, alleviating symptoms, and preventing disease progression.
Pharmacological Treatments
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to manage the symptoms of chronic prostatitis and BPH. These medications help reduce pain and inflammation but may not address the underlying causes. For more targeted therapy, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which block the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, have been shown to reduce prostate size and alleviate symptoms in BPH patients.
In cases where inflammation is linked to infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. However, the efficacy of antibiotics in treating non-bacterial chronic prostatitis remains limited, highlighting the need for alternative approaches.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle interventions play a crucial role in managing chronic prostate inflammation. Diet and exercise are key factors that can influence inflammation levels. Diets rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce systemic inflammation. Regular physical activity has also been shown to decrease inflammatory markers and improve overall prostate health.
Emerging Therapies
The field of prostate health is witnessing the development of novel therapies aimed at targeting the molecular pathways involved in chronic inflammation. For instance, inhibitors of the NF-?B pathway are being investigated for their potential to reduce inflammation and prevent prostate cancer progression. Additionally, antioxidant therapies are being explored to counteract oxidative stress and its detrimental effects on prostate tissue.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation is a significant contributor to prostate health issues in American males, influencing the development and progression of conditions such as chronic prostatitis, BPH, and prostate cancer. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms of chronic prostate inflammation is essential for developing effective therapeutic interventions. While current treatments focus on symptom management and reducing inflammation, ongoing research into novel therapies offers hope for more targeted and effective strategies to improve prostate health and quality of life for American males.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Prostate Health in Aging American Men: Understanding Conditions and Maintaining Wellness [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Prostate Health: Key Foods to Reduce Cancer Risk and Promote Wellness [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Family History and Prostate Health: Understanding Genetic Risks and Early Detection [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Prostate Health and Heart Disease: Vital Connections for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer Survivorship: Navigating Life After Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Enhancing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer's Psychological Impact on American Men: Diagnosis to Survivorship [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer Screening: Balancing Benefits and Risks with Informed Decision-Making [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Prostate Health: Understanding Symptoms, Seeking Care, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer Treatments: Understanding and Managing Side Effects in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Symptoms, Causes, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Prostate Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Prostate Health: Risks, Diet, Exercise, and Early Detection Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer's Impact on Fertility: Treatments and Preservation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise and Diet: Enhancing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption's Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Moderation Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Radiation Therapy: A Key Treatment for Prostate Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormone Therapy's Role in Managing Prostate Cancer for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Prostate Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer: Navigating Diagnosis and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Immunotherapy Revolutionizing Prostate Cancer Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Pesticides and Prostate Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Active Surveillance: Managing Low-Risk Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Targeted Therapy: A New Hope in Prostate Cancer Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Avoiding Key Foods to Maintain Prostate Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Brachytherapy: Targeted Treatment for Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- HIFU: A Promising Non-Invasive Treatment for Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Key to Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Proton Therapy: A Targeted Approach to Prostate Cancer Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chemotherapy's Role and Impact on American Men with Prostate Cancer [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Antioxidants and Prostate Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Quality's Impact on Prostate Health: A Vital Connection for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Their Impact on Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Lycopene: A Key Nutrient for Prostate Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer Stages and Grades: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation's Impact on Prostate Health in American Males: Prevention and Awareness [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Heavy Metals and Prostate Health: Risks, Impacts, and Preventive Measures [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- CyberKnife: Advanced Non-Invasive Treatment for Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Prostate and Bone Health: Vital Connections and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Palliative Care's Vital Role in Enhancing Prostate Cancer Patients' Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hydration's Vital Role in Prostate Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer and Cryotherapy: A Minimally Invasive Treatment Option for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Vitamin E's Role in Prostate Health: Benefits and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Photodynamic Therapy: A Promising, Less Invasive Treatment for Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Selenium's Role in Prostate Health: Benefits and Dietary Sources [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Plastics' Impact on Prostate Health: BPA, Phthalates, and Preventive Measures [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Zinc's Vital Role in Prostate Health for American Males: Benefits and Sources [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Green Tea Benefits for Prostate Health in American Males: Prevention and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Chemoprevention Strategies for Prostate Cancer Prevention in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Air Pollution's Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer Management: Understanding Watchful Waiting for Low-Risk Patients [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer Surgery: Understanding Radical Prostatectomy and Its Impact [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Enhancing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- EMF Exposure and Prostate Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Robotic Surgery for Prostate Cancer: Benefits, Procedure, and Recovery Insights [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Focal Therapy: A Promising, Less Invasive Option for Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disruptors and Prostate Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A Minimally Invasive Option for Prostate Cancer Treatment [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Salvage Therapy: A Critical Approach to Managing Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Industrial Chemicals' Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Flaxseed Benefits for Prostate Health: Cancer Prevention and BPH Relief [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Soy Isoflavones: A Dietary Approach to Enhancing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Prostate Health Management: Balancing Pharmaceuticals and Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Pomegranate's Role in Enhancing Prostate Health: Nutritional Benefits and Research Insights [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Palliative Surgery for Advanced Prostate Cancer: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Neoadjuvant Therapy in Prostate Cancer: Benefits, Side Effects, and Future Directions [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Adjuvant Therapy in Prostate Cancer: Enhancing Outcomes and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Bisphosphonates: Enhancing Bone Health in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Denosumab: A Promising Treatment for Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- RANK Ligand Inhibitors: A Promising Therapy for Prostate Cancer Bone Metastases [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Heavy Physical Work's Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Radium-223: A Targeted Therapy for Advanced Prostate Cancer in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Abiraterone: Revolutionizing Prostate Cancer Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Enzalutamide: A Key Advance in Prostate Cancer Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Ginger's Role in Supporting Prostate Health: Benefits and Dietary Integration [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Turmeric's Potential Benefits for Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Prostate Health Risks and Mitigation Strategies for Long-Haul Truckers [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Obesity's Impact on Prostate Health: A 15-Year Epidemiological Analysis in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]