Introduction
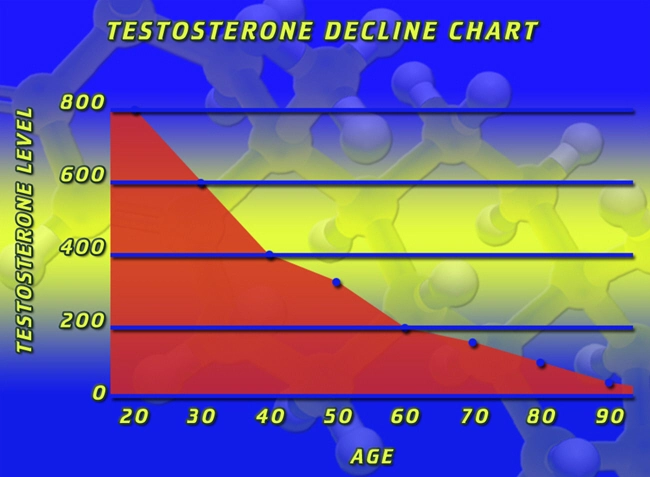
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in maintaining various physiological functions, including muscle mass, bone density, and sexual health. Recent studies have highlighted the potential association between low testosterone levels and the development of endocrine disorders in American men. This article aims to explore the findings of a cross-sectional study that investigated the relationship between low testosterone and endocrine disorders, with a focus on hormonal assays and their implications for male health.
Study Methodology and Participant Selection
The cross-sectional study involved a diverse cohort of American males aged 30 to 70 years. Participants were selected based on their willingness to undergo comprehensive hormonal assessments and provide detailed medical histories. The study employed rigorous exclusion criteria to minimize confounding factors, such as the presence of known endocrine disorders at baseline or the use of medications that could affect testosterone levels.
Hormonal Assays and Data Collection
Hormonal assays were conducted using state-of-the-art laboratory techniques to measure total testosterone, free testosterone, and other relevant hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Blood samples were collected in the early morning to account for diurnal variations in hormone levels. Additionally, participants completed questionnaires to assess symptoms related to low testosterone and potential endocrine disorders.
Prevalence of Low Testosterone and Endocrine Disorders
The study revealed a significant prevalence of low testosterone among the participants, with approximately 25% of men exhibiting levels below the established reference range. Furthermore, a notable association was observed between low testosterone and the development of endocrine disorders, such as type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and hypogonadism. The data suggested that men with low testosterone were at a higher risk of developing these conditions compared to their counterparts with normal testosterone levels.
Mechanisms Linking Low Testosterone to Endocrine Disorders
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the link between low testosterone and the development of endocrine disorders. One potential pathway involves the impact of low testosterone on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, which may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Additionally, low testosterone has been associated with increased fat mass and decreased lean body mass, further exacerbating the risk of metabolic disorders.
Another mechanism involves the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which regulates testosterone production. Dysregulation of this axis, as evidenced by elevated LH and FSH levels in some participants, may contribute to the development of hypogonadism and other endocrine disorders.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The findings of this study have significant clinical implications for the management of low testosterone and the prevention of endocrine disorders in American men. Healthcare providers should consider routine testosterone screening for men at risk of developing these conditions, particularly those with symptoms suggestive of low testosterone. Early detection and appropriate management of low testosterone may help mitigate the risk of developing endocrine disorders and improve overall health outcomes.
Future research should focus on longitudinal studies to establish causality between low testosterone and endocrine disorders. Additionally, investigating the efficacy of testosterone replacement therapy in preventing or managing these conditions could provide valuable insights for clinical practice.
Conclusion
The cross-sectional study highlights the significant association between low testosterone and the development of endocrine disorders in American men. The findings underscore the importance of hormonal assessments in identifying individuals at risk and implementing targeted interventions. By addressing low testosterone and its potential consequences, healthcare providers can contribute to the overall well-being and quality of life of American males.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Environmental Toxins Linked to Low Testosterone in American Men: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone: Symptoms, Risks, and Comprehensive Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone: Risks and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Chronic Illnesses and Low Testosterone: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Men's Health and Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impacts and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: Strategies for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Interlinked Challenges and Management Strategies for Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Effects on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Osteoporosis: Risks, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Boosting Testosterone in American Men: The Power of Physical Activity and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Understanding Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Mechanisms and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone: What American Men Need to Know and Manage [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on American Males' Body Composition and Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease Risk in American Men: Current Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain and Low Testosterone: A Critical Health Issue for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens and Declining Testosterone in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Dietary Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Insights and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Male Libido: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Low Levels [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression in American Men: Links, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Risks and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Thyroid Disorders: Exploring Risks and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Anemia: Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on American Men's Testosterone Levels and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Liver Health and Testosterone: Vital Connections and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalance and Low Testosterone: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Low Testosterone: Impacts and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: A Growing Concern for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Autoimmune Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutritional Deficiencies Impacting Testosterone Levels in American Males: Zinc, Vitamin D, Magnesium [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Disorders in American Men: Research and Implications [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Gut Microbiome's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Emerging Insights [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Dermatological Issues in American Men: Research and Management [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Reproductive Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Men: Interventions and Insights [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- ENT Health and Testosterone: Managing Conditions to Boost Hormonal Balance in Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Detection, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Hematological Risks in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Higher Infection Risk in American Men: Research Insights [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Testosterone: A Holistic Endocrine Approach [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Immune System's Role in Testosterone Levels: Impacts and Interventions for American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Risks in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Surgical Risks in American Men: Implications and Recommendations [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Clinical Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Rheumatological Conditions and Low Testosterone: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels and Wound Healing in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Vascular Disorders: Risks, Mechanisms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Anesthetics' Impact on Testosterone: Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Genetic Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Early Life Health Factors Impact Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Pediatric Disorders in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Geriatric Risks in American Men: Detection and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Prenatal Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Allergic Reactions in American Men: Emerging Insights [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Congenital Disorders in American Men: Research Insights [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Neonatal Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Occupational Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Stress, Work Demands, and Environment [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Diagnosis, HRT, Lifestyle, and Psychological Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Impacts, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]