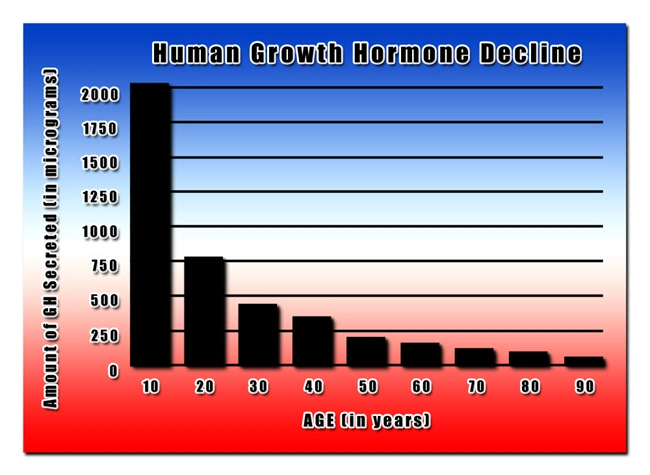
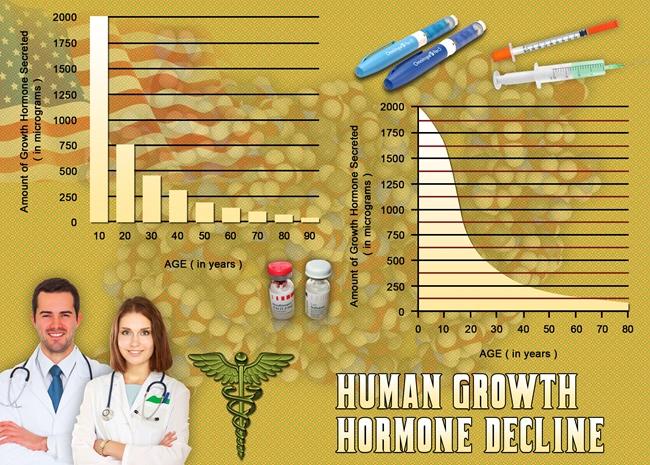
Introduction
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has been increasingly recognized as a significant health concern among American males. Recent research has begun to explore its potential impacts on various aspects of male health, including prostate function. This article delves into a multicenter study that examines the intricate relationship between hormonal imbalances caused by secondary hypogonadism and prostate health, offering valuable insights for both medical professionals and patients.
Study Overview and Methodology
The multicenter study involved over 1,000 American males aged between 40 and 70 years, diagnosed with secondary hypogonadism. Researchers meticulously assessed their hormonal profiles, focusing on testosterone levels, and correlated these with various indicators of prostate health, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, digital rectal examination (DRE) findings, and prostate volume measured by transrectal ultrasound. The aim was to determine whether there is a significant association between low testosterone levels due to secondary hypogonadism and alterations in prostate function.
Findings on Hormonal Levels and Prostate Health
The study revealed a notable trend: men with lower testosterone levels due to secondary hypogonadism exhibited higher PSA levels and larger prostate volumes compared to those with normal testosterone levels. This suggests a potential link between secondary hypogonadism and an increased risk of prostate enlargement, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Additionally, the study found that participants with more severe hypogonadism were more likely to have abnormal DRE findings, further indicating a possible impact on prostate health.
Implications for Prostate Cancer Risk
One of the critical concerns addressed in the study was the potential relationship between secondary hypogonadism and prostate cancer risk. While the study did not establish a direct causal link, it noted that men with lower testosterone levels had a slightly higher incidence of prostate cancer compared to those with normal levels. This finding underscores the importance of regular prostate screenings for men diagnosed with secondary hypogonadism, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Clinical Management and Treatment Considerations
Given the study's findings, clinicians are encouraged to consider the implications of secondary hypogonadism on prostate health when managing patients. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), commonly used to treat hypogonadism, must be approached with caution. The study suggests that while TRT can help alleviate symptoms of low testosterone, it may also influence prostate health. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of prostate health should be conducted before initiating TRT, and patients should be closely monitored throughout the treatment process.
Future Research Directions
The study opens several avenues for future research. Further investigations are needed to better understand the mechanisms through which secondary hypogonadism affects prostate health and to explore potential preventive strategies. Longitudinal studies could provide more definitive data on the long-term effects of low testosterone on prostate function and cancer risk. Additionally, research into alternative treatments for secondary hypogonadism that do not adversely affect prostate health could offer new therapeutic options for affected men.
Conclusion
The multicenter study provides compelling evidence of a relationship between secondary hypogonadism and prostate health in American males. As the prevalence of hypogonadism continues to rise, understanding its impact on prostate function becomes increasingly crucial. This study not only highlights the need for integrated care approaches in managing hypogonadism but also emphasizes the importance of proactive prostate health monitoring in affected men. By fostering a deeper understanding of this complex relationship, healthcare providers can better tailor treatments to improve the overall health and quality of life of their patients.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Psychological Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Support Systems Crucial for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Pituitary Gland's Role and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Understanding and Managing the Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Factors Driving Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Importance of Early Detection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders in American Men: Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Fatigue in American Males with Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Medical Interventions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: A Critical Connection for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Treatment Implications in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Strength and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Insights and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Causes, Effects, and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Hormonal Therapies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Role of Diet in Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Health and Relationships in America [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Holistic Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management for American Men's Daily Life [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Personalized Treatment [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Vitality and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Impact and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Boosting Testosterone Naturally [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]