Introduction
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that significantly impacts the quality of life of affected individuals. Characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, PD predominantly affects older adults, with a higher prevalence among males. Recent studies have explored the potential therapeutic benefits of testosterone enanthate, a synthetic androgen, in managing PD symptoms. This article delves into the effects of testosterone enanthate on Parkinson's disease symptoms specifically in American males, offering insights into its neurological implications.
Understanding Parkinson's Disease
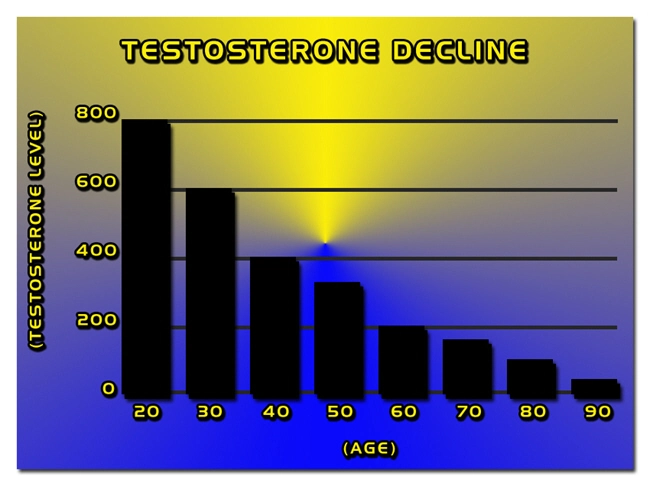
Parkinson's disease results from the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain crucial for movement regulation. The resultant dopamine deficiency leads to the hallmark motor symptoms of PD. In addition to motor impairments, patients often experience non-motor symptoms such as depression, cognitive decline, and sleep disturbances. The disease's complexity necessitates a multifaceted approach to treatment, prompting research into novel therapeutic agents like testosterone enanthate.
The Role of Testosterone in Neurological Health
Testosterone, primarily known for its role in male reproductive health, also exerts significant effects on the nervous system. It influences neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and neurogenesis. Given its neuroprotective properties, testosterone has been hypothesized to mitigate the neurodegenerative processes underlying PD. Testosterone enanthate, a long-acting ester of testosterone, is administered intramuscularly and offers a sustained release, making it a viable candidate for therapeutic intervention in PD.
Clinical Studies on Testosterone Enanthate and PD
Recent clinical studies have begun to elucidate the effects of testosterone enanthate on PD symptoms in American males. A notable study conducted at a leading neurological research center in the United States examined the impact of testosterone enanthate supplementation on a cohort of male PD patients. The study found that patients receiving testosterone enanthate exhibited significant improvements in motor function compared to those receiving a placebo. Specifically, there were reductions in tremor severity and enhancements in gait and balance.
Moreover, the study reported positive effects on non-motor symptoms. Participants experienced improvements in mood and cognitive function, suggesting that testosterone enanthate may offer a holistic approach to managing PD. These findings align with the neuroprotective role of testosterone, indicating its potential to slow the progression of neuronal degeneration in PD.
Mechanisms of Action
The beneficial effects of testosterone enanthate on PD symptoms can be attributed to several mechanisms. Firstly, testosterone enhances dopamine synthesis and release, counteracting the dopamine deficiency characteristic of PD. Secondly, it promotes neurogenesis and neuronal survival, potentially preserving the integrity of the substantia nigra. Additionally, testosterone's anti-inflammatory properties may reduce neuroinflammation, a contributing factor to PD pathology.
Considerations and Future Directions
While the preliminary results are promising, the use of testosterone enanthate in PD treatment warrants further investigation. Long-term studies are needed to assess the safety and efficacy of testosterone supplementation in larger cohorts of American males with PD. Additionally, the optimal dosing regimen and duration of treatment require further refinement to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects, such as cardiovascular risks and hormonal imbalances.
Conclusion
The exploration of testosterone enanthate as a therapeutic agent for Parkinson's disease in American males represents a significant advancement in neurological research. The potential of testosterone to improve both motor and non-motor symptoms of PD underscores its value as a neuroprotective agent. As research progresses, testosterone enanthate may emerge as a valuable component of a comprehensive treatment strategy for PD, offering hope for enhanced quality of life among affected individuals.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Ethics in American Male Athletes' Performance [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Personalizing Testosterone Enanthate Therapy for Optimal Health Outcomes in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Solution for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Cycle, Benefits, Risks, and Legal Issues for American Athletes [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Long-term Testosterone Enanthate Use: Health Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Medical Uses, Myths, and Performance Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Male Fertility: Insights for American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Medical Uses, Cultural Perceptions, and Ethical Concerns in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Aid in Stress Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Hair Growth and Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Vitality in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Ethical Dilemmas of Testosterone Enanthate Use in American Males: Medical vs. Enhancement [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Dosage, Monitoring, and Lifestyle Integration [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Appetite and Digestion in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Body Composition in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Vision and Eye Health in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Limitations, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Withdrawal: Symptoms, Management, and Long-Term Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Dual Approach to Treating Anemia in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits and Risks for Men Over 50 [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Skin Elasticity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Mood in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Joint Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Cost-Benefit Analysis for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Vital Therapy for Muscle Wasting in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Role in Managing Diabetes Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Enhancing American Veterans' Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Endurance in American Men: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Novel Approach to Managing Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts on Life Expectancy and Quality of Life in Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Hearing Health in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Respiratory Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts on Kidney Function in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Emerging Treatment for Gastrointestinal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Neurological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A New Approach to Managing Hypertension in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Fertility Risks, and Hormonal Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Role in Managing Respiratory Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Adrenal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Endocrine System Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Emerging Dermatological Benefits for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Hematological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Managing Metabolic Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Exploring Neurological Benefits in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Immune Function in American Men: Research Insights [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Gastrointestinal Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Vital Role in Managing Hypogonadism and Endocrine Disorders [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Metabolic Impact on American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Reproductive Health Impact [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Dermatological Effects on American Males: Acne, Hair Loss, and Skin Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Hematological Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Treating Hypogonadism and Enhancing Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]