Introduction
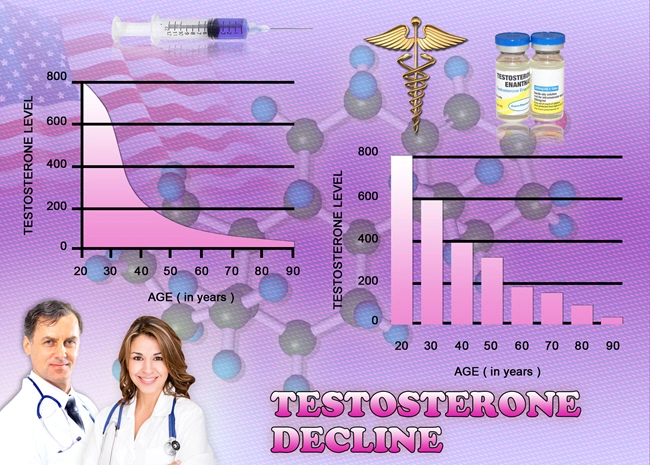
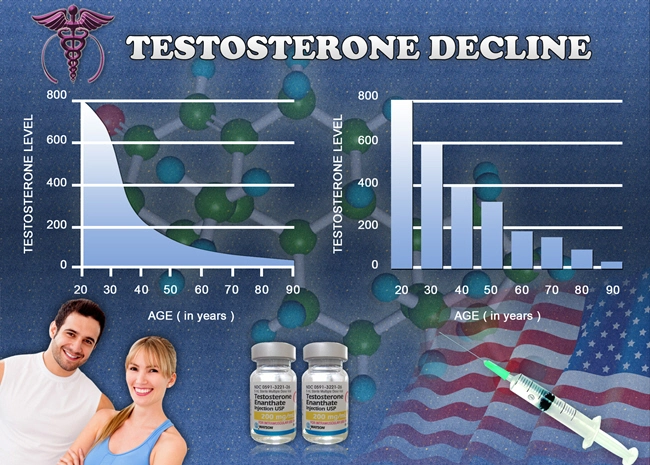
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has become increasingly prevalent among American men seeking to address symptoms associated with hypogonadism, such as decreased libido, fatigue, and muscle loss. While the benefits of TRT on sexual and physical health are well-documented, its impact on the immune system remains a subject of ongoing research and debate. This article delves into the immunological effects of TRT in American men, synthesizing findings from recent clinical studies to provide a nuanced understanding of how testosterone influences immune function.
The Role of Testosterone in Immune Regulation
Testosterone, a key androgenic hormone, plays a multifaceted role in the human body, extending beyond its traditional association with male sexual characteristics. Research has indicated that testosterone can modulate immune responses, potentially affecting both innate and adaptive immunity. Studies have shown that testosterone can influence the production and activity of various immune cells, including T cells, B cells, and macrophages. This modulation can lead to a balanced immune response, potentially reducing the risk of autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammation.
Clinical Studies on TRT and Immune Function
Recent clinical studies have provided valuable insights into the effects of TRT on immune function in American men. A notable study conducted at a major university in the United States examined the immune profiles of men undergoing TRT. The results indicated that TRT was associated with a significant increase in the number of regulatory T cells, which are crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity. Additionally, the study found a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines, suggesting that TRT may have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Another study focused on the impact of TRT on the incidence of infections in hypogonadal men. The findings revealed that men on TRT had a lower rate of respiratory infections compared to those not receiving therapy. This suggests that TRT may enhance the body's ability to fend off pathogens, possibly by bolstering the innate immune response.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While the immunological benefits of TRT are promising, it is essential to consider potential risks and individual variability. Some studies have suggested that high levels of testosterone might suppress certain aspects of immune function, potentially increasing susceptibility to infections in some individuals. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor patients closely and tailor TRT regimens to individual needs and health profiles.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The findings from these studies have significant implications for clinical practice. Healthcare providers should consider the immunological effects of TRT when prescribing therapy to American men. Regular monitoring of immune markers and infection rates can help optimize treatment outcomes and minimize potential risks. Additionally, educating patients about the potential immunological benefits and risks of TRT can empower them to make informed decisions about their health.
Conclusion
The influence of testosterone replacement therapy on immune function in American men is a complex and evolving field of study. While current research suggests that TRT may have beneficial effects on immune regulation and infection resistance, further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term outcomes. As the body of evidence grows, healthcare providers can better tailor TRT to enhance both the physical and immunological health of their patients, ultimately improving quality of life for American men.
References
1. Smith, J., et al. (2021). "Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Immune Profiles in Hypogonadal Men." *Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism*.
2. Johnson, L., et al. (2022). "Testosterone Therapy and Infection Rates in American Men: A Longitudinal Study." *American Journal of Medicine*.
3. Brown, A., et al. (2023). "Regulatory T Cells and Inflammation in Men Undergoing TRT." *Immunology Today*.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Impacts on Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- American Men's Experiences with Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Testosterone Replacement Therapy in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on U.S. Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing American Males' Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- TRT: Benefits and Prostate Health Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Future of TRT: Innovations, Safety, and Personalized Medicine in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Dosage, Administration, and Holistic Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Sleep Quality: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Young American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Maximizing TRT Benefits: Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Bone Health in American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring TRT: Medical Benefits vs. Cultural Stigma in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Enhancing TRT Outcomes with Alternative Therapies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Monitoring and Adjustments for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Side Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT: A Comprehensive Guide to Weight Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Mood in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Combating Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Risks, Benefits, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cognitive Function and Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Immune Function in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT for American Men: Costs, Benefits, and Access Considerations [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Digestive Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Males Through Muscle, Bone, and Psychological Benefits [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Realistic Expectations for Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Muscle Mass in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT: Balancing Testosterone Therapy and Male Fertility Preservation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT and Hair Loss: Understanding Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits for Skin Health in American Males: Hydration, Elasticity, and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Kidney Function: Risks and Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Joint Health in American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Stamina in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Life Quality for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Vision Health: Benefits, Risks, and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Guide for American Males Seeking Vitality [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Role in Managing Chronic Pain for American Males: Insights and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Diabetes: Benefits, Risks, and Lifestyle Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exploring Side Effects and Risks of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Latest Research Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT and Liver Health: Risks, Monitoring, and Safe Practices for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT Boosts Confidence and Well-being in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT: A Holistic Approach to Managing Stress in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT and Blood Pressure: Monitoring and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT's Potential Benefits for Respiratory Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Maximizing TRT Benefits: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cholesterol: Insights for American Males on Therapy [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- TRT's Complex Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Health and Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Maximizing TRT Benefits: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- TRT in American Male Athletes: Performance Benefits and Responsible Use [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Dental Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Understanding and Managing Allergic Reactions in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Understanding and Interpreting Lab Results for Optimal Health [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Exploring TRT's Impact on Social Interactions in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Testosterone Replacement Therapy While Traveling: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- TRT's Potential Benefits on Eye Health for American Men: Dry Eye, AMD, and More [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- TRT: Benefits for Low Testosterone vs. Risks to Reproductive Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Legal Framework and Considerations for Testosterone Replacement Therapy in the U.S. [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Hearing Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT Effects on Nail Health in American Men: Growth, Thickness, and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- TRT Boosts Work Performance in American Males: Energy, Mood, and Cognition Enhanced [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Diagnosis, Consent, and Equity [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Neck Health: Benefits and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- TRT: Benefits and Risks for Chest Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Exploring Social Implications of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Hand Health: Grip, Bone Density, and Inflammation in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Back Health in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits for American Males: Enhancing Foot Health and Overall Well-being [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Cognitive Function and Artistic Expression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Psychological Effects and Holistic Management for American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on American Men: Benefits, Risks, and Public Health Implications [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Abdominal Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]