Introduction
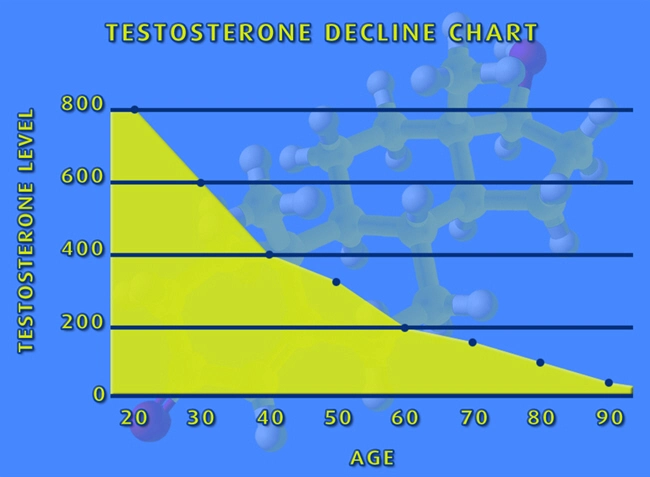
Testosterone Cypionate, a commonly prescribed testosterone replacement therapy, has been a subject of interest in the medical community due to its potential impact on male fertility and sperm quality. As the prevalence of testosterone deficiency rises among American men, understanding the implications of such treatments on reproductive health becomes increasingly important. This article delves into a prospective cohort study that examines the effects of Testosterone Cypionate on male fertility and sperm quality in the American male population, offering insights that could guide clinical decision-making and patient counseling.
Study Design and Methodology
The study in question adopted a prospective cohort design, following a group of American men aged 30 to 50 years who were prescribed Testosterone Cypionate for hypogonadism. Participants underwent comprehensive assessments at baseline and at regular intervals over a two-year period. Key parameters measured included serum testosterone levels, semen analysis for sperm concentration, motility, and morphology, as well as fertility outcomes such as conception rates among partners.
Impact on Serum Testosterone Levels
Upon initiation of Testosterone Cypionate therapy, participants experienced a significant increase in serum testosterone levels, which stabilized within the normal range for most subjects. This elevation in testosterone is crucial for addressing symptoms of hypogonadism but raised concerns about potential suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which could affect fertility.
Effects on Sperm Quality and Concentration
The study found a notable decline in sperm concentration and motility among participants following the commencement of Testosterone Cypionate treatment. Sperm morphology, an important indicator of fertility potential, also showed deterioration in a significant proportion of the cohort. These findings suggest that while Testosterone Cypionate effectively raises testosterone levels, it may compromise sperm quality, potentially impacting male fertility.
Fertility Outcomes
An analysis of fertility outcomes revealed a decrease in conception rates among the partners of study participants. This reduction in fertility aligns with the observed declines in sperm parameters, highlighting a potential risk for men on Testosterone Cypionate who are planning to conceive. The study underscores the importance of discussing fertility preservation options with patients prior to starting therapy.
Clinical Implications and Recommendations
The findings of this study have significant clinical implications for American men considering or currently undergoing Testosterone Cypionate therapy. Healthcare providers should engage in thorough discussions with patients about the potential impact on fertility and consider alternative treatments for those wishing to preserve reproductive potential. For men already on therapy who are planning to conceive, temporary cessation of Testosterone Cypionate and the use of fertility-enhancing medications may be warranted.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to explore the reversibility of the effects of Testosterone Cypionate on sperm quality and fertility upon discontinuation of the therapy. Additionally, investigating the efficacy of adjunctive treatments to mitigate the negative impacts on reproductive health could provide valuable insights. Long-term studies with larger cohorts would also enhance our understanding of the broader implications of testosterone therapy on male reproductive health.
Conclusion
This prospective cohort study provides critical evidence of the impact of Testosterone Cypionate on male fertility and sperm quality among American men. While the therapy effectively addresses hypogonadism, it poses potential risks to reproductive health that must be carefully weighed. As the medical community continues to refine its approach to testosterone replacement therapy, the findings of this study will play a pivotal role in shaping clinical practice and informing patient care.
In summary, while Testosterone Cypionate offers significant benefits for men with hypogonadism, its impact on fertility and sperm quality necessitates a balanced approach to treatment, prioritizing informed consent and individualized patient management strategies.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Testosterone Cypionate: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Management for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Male Health Through Injection Therapy [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Sleep Patterns in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate Stigma in American Males: Origins, Impacts, and Destigmatization Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Strategies to Minimize Side Effects of Testosterone Cypionate in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance for Testosterone Cypionate Therapy: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Impacts on Prostate Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Benefits, Risks, and Long-Term Health Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men: Experiences and Insights [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate Therapy: Costs, Coverage, and Financial Planning for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Managing Chronic Conditions in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Effects on Skin Health and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Monitoring Testosterone Cypionate Levels: Essential Guide for Safe TRT in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Dual Benefit for Diabetes Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Debunking Myths and Clarifying Facts for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Hearing in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Vital Tool for American Transgender Males' Transition [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Libido in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Legal Status and Usage Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Blood Pressure in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Benefits, Risks, and Safety for American Males on TRT [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Vision Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Role in Injury Recovery: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Red Blood Cell Production in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Muscle Growth Benefits vs. Joint Health Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate and Hair Loss in American Males: Mechanisms, Risks, and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Liver Function in American Males: Risks and Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Novel Treatment for Skin Conditions in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Boosting Energy Levels in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Neurological Impacts and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Uses, Benefits, and Safe Usage for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Eye Health: Benefits and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Lung Function in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Kidney Health in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate and Male Pattern Baldness: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Digestive Health in American Men: An Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Novel Approach to Managing Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Exploring Pain Management Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Dental Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Treatment for Respiratory Conditions in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Effects on Endocrine System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Effects on Urinary System and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Fertility in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Managing Metabolic Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Immune Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Therapy for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Role in Managing Hematological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Dermatological Effects on American Men: Acne, Hair Loss, and Skin Aging [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Renal Health in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Impacts on Genitourinary System and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Muscle and Bone Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Mental Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Hematological System: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: A Promising Treatment for Respiratory Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Emerging Dermatological Uses and Considerations in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Neurological Impacts on American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Uses, Mechanism, and Safety in Treating Endocrine Disorders [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Impacts on Endocrine System and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Psychiatric Effects of Testosterone Cypionate in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Effective Hypogonadism Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate: Enhancing Muscle and Bone Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Cypionate's Role in Managing Metabolic Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]