Introduction
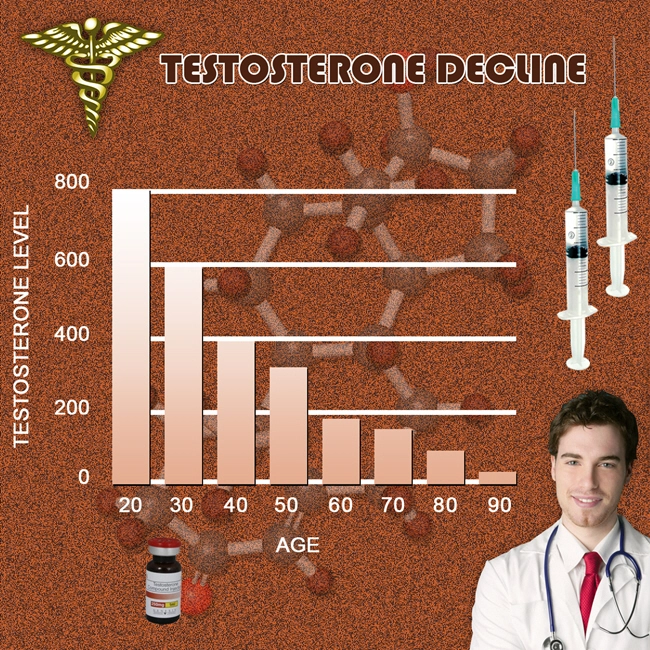
Andropause, colloquially known as male menopause, is a term used to describe the gradual decline in testosterone levels in aging men. This hormonal shift can lead to a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, mood swings, and decreased libido. Recent research has begun to explore the potential impact of andropause on other bodily functions, such as auditory health. This article delves into a longitudinal study that examines the correlation between hormonal changes associated with andropause and hearing loss in American males, providing insights that could enhance the understanding and management of age-related hearing decline.
Study Design and Methodology
The study in question followed a cohort of 1,200 American males aged 40 to 70 over a period of 10 years. Participants were assessed annually for testosterone levels, and their hearing was evaluated using audiometric tests. The study aimed to identify any patterns linking the decline in testosterone with changes in auditory function. Data analysis included statistical methods to account for variables such as age, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions.
Findings: Hormonal Changes and Hearing Loss
The results of the study indicated a significant association between declining testosterone levels and the onset of hearing loss. Men who experienced a more rapid decrease in testosterone were more likely to develop hearing impairments earlier than those with a slower decline. Specifically, the study found that for every 10% drop in testosterone levels, the risk of developing hearing loss increased by approximately 15%. These findings suggest that the hormonal changes associated with andropause may play a role in the deterioration of auditory function.
Mechanisms Behind the Correlation
Several biological mechanisms may explain the link between andropause and hearing loss. Testosterone receptors are present in the inner ear, suggesting that testosterone may influence the health and function of auditory cells. A decline in testosterone could lead to reduced blood flow to the inner ear, increased oxidative stress, or changes in the cellular structure of the cochlea, all of which could contribute to hearing loss. Further research is needed to fully understand these mechanisms, but the current findings highlight the potential impact of hormonal changes on auditory health.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The study's findings have significant implications for clinical practice. Healthcare providers should consider monitoring testosterone levels in middle-aged and older men, particularly those who report hearing difficulties. Early detection of andropause and its associated symptoms could lead to timely interventions, such as hormone replacement therapy, which may help mitigate the risk of hearing loss. Additionally, men experiencing symptoms of andropause should be informed about the potential impact on their auditory health and encouraged to undergo regular hearing assessments.
Future Research Directions
While this study provides valuable insights into the relationship between andropause and hearing loss, further research is necessary to confirm and expand upon these findings. Future studies should explore the effectiveness of testosterone supplementation in preventing or slowing the progression of hearing loss in men with low testosterone levels. Additionally, research should investigate whether other hormonal changes associated with aging contribute to auditory decline, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing hearing health in older males.
Conclusion
The longitudinal study on andropause and hearing loss in American males reveals a compelling correlation between declining testosterone levels and the risk of developing hearing impairments. These findings underscore the importance of considering hormonal factors in the management of age-related hearing loss. By integrating this knowledge into clinical practice, healthcare providers can offer more personalized and effective care to men navigating the challenges of andropause and its potential impact on their auditory health.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- 0001) Understanding Andropause: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- 0002) Andropause: Debunking Myths and Understanding Realities for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- 0003) Andropause and Prostate Health: Navigating the Complex Link for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0004) Exploring Supplements for Andropause: Efficacy, Safety, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0005) Managing Andropause: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0006) Andropause and Cognitive Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Mental Sharpness [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0007) Andropause Management: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Aging Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0008) Navigating Andropause: Emotional Well-being and Support for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0009) Andropause in American Males: Symptoms, Diabetes Risk, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0010) Andropause: Navigating Social Impacts and Support for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0011) Andropause Effects on Skin: Essential Skincare Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0012) Andropause: Understanding Symptoms and Embracing Growth in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0013) Navigating Andropause: Emotional Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0014) Andropause: Mental Health Professionals' Role in Managing Male Menopause Symptoms [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0015) Andropause Effects on Joint Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0016) Andropause in American Men: Benefits and Risks of Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0017) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Managing Its Effects [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0018) Andropause and Depression in American Men: Symptoms, Links, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0019) Managing Andropause: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0020) Andropause: Impact on American Men's Self-Esteem and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0021) Andropause: Understanding Symptoms, Family Support, and Healthy Lifestyle Changes for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0022) Andropause and Hair Loss: Understanding Causes and Exploring Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0023) Andropause: Navigating Male Menopause with Essential Support Networks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0024) Andropause: Understanding and Managing Male Menopause in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0025) Managing Andropause: Combating Fatigue with Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0026) Andropause and Immune Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Well-being [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0027) Andropause and Digestive Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0028) Andropause and Memory: Strategies for American Males to Enhance Cognitive Function [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0029) Andropause: Managing Muscle Loss in American Males Through Exercise and Nutrition [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0030) Andropause and Cholesterol Management in American Males: Diet, Exercise, and Medical Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0031) Andropause: Managing Symptoms and Work Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0032) Andropause and Vision: Managing Eye Health in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0033) Navigating Andropause: Essential Nutrition for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0034) Hydration's Crucial Role in Managing Andropause Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0035) Andropause and Kidney Health: Understanding the Link and Managing Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0036) Andropause and Energy: Understanding and Managing Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0037) Andropause and Thyroid Function: Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0038) Andropause and Dental Health: Tips for American Males to Maintain Oral Hygiene [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0039) Andropause Impact on Liver Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0040) Mindfulness: A Key Strategy for Managing Andropause Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0041) Andropause and Blood Pressure: Monitoring and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0042) Community Support Enhances American Men's Andropause Management and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0043) Andropause in American Males: Symptoms, Stress Management, and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0044) Andropause Management: The Vital Role of Sleep for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0045) Andropause: Understanding Declining Testosterone's Impact on American Men's Motivation and Drive [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0046) Andropause and Respiratory Health: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0047) Andropause: Managing Mental Health with Essential Mental Health Days for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0048) Andropause Management: Exercise Benefits for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0049) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Impact on American Men's Confidence [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0050) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Essential Health Screenings for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0051) Andropause and Emotional Intelligence: Enhancing Men's Well-being [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0052) Andropause and Hearing Loss: Understanding the Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- 0053) Andropause Management: The Therapeutic Role of Hobbies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- 0054) Andropause and Creativity: Managing Decline in American Men's Cognitive Output [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- 0055) Andropause and Allergies: Managing Symptoms for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- 0056) Managing Andropause: Goal Setting for American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- 0057) Andropause and Skin Sensitivity: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- 0058) Andropause: Understanding Its Impact on American Men's Purpose and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0059) Andropause and Foot Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Mobility and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- 0060) Andropause: Managing Symptoms with Time Management and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- 0061) Technology Revolutionizes Andropause Management for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0062) Andropause: Navigating Declining Testosterone and Maintaining an Adventurous Life [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0063) Andropause Impact on Nail Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0064) Volunteering: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause Symptoms in Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0065) Andropause Impact on Eye Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0066) Andropause: Managing Its Impact on Hand Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0067) Andropause and Lifelong Learning: Empowering American Men's Health Journey [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0068) Travel as Therapy: Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- 0069) Andropause and Ear Health: Protecting Hearing in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0070) Andropause Effects on Oral Health: Managing Tongue and Saliva Changes in Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0071) Andropause in American Males: Understanding Its Impact on Nose Health [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- 0072) Music Therapy: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0073) Andropause Management: Harnessing Art for Psychological and Cognitive Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0074) Andropause Impact on Throat Health: Symptoms and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0075) Andropause: Financial Planning Strategies for American Men's Health and Retirement [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0076) Andropause: Impact on American Men's Humor and Cultural Identity [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0077) Andropause: Navigating Identity and Masculinity in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0078) Andropause in American Men: Enhancing Life with Social Connections [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0079) Understanding Andropause: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- 0080) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Impact on Belonging in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]