Introduction
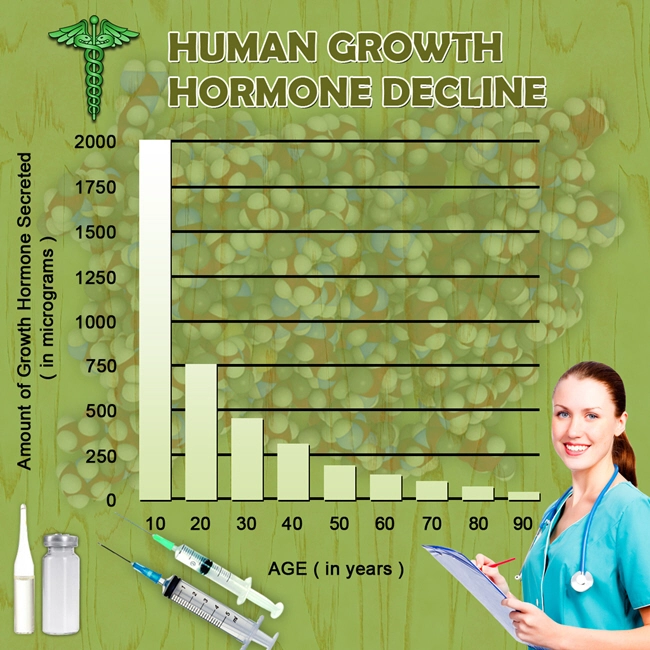
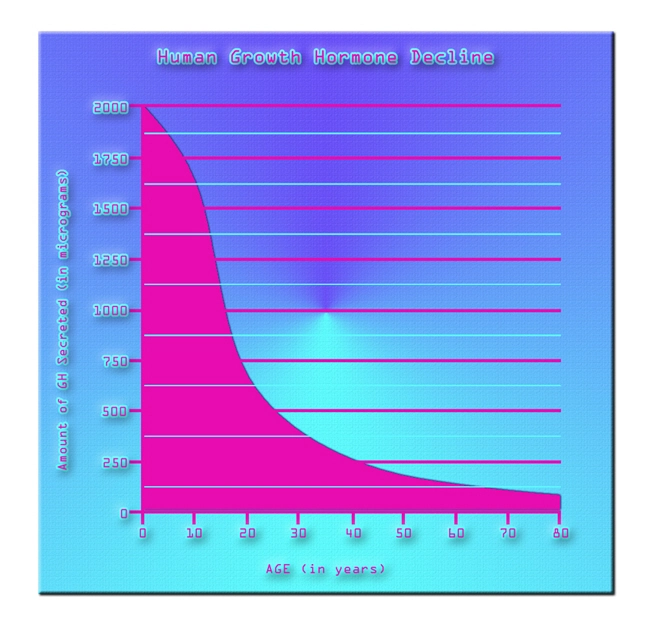
Andropause, commonly known as male menopause, represents a gradual decline in testosterone levels that occurs in aging men. This physiological transition has been increasingly recognized for its potential impact on various organ systems, including the liver. Over the past two decades, research has begun to elucidate the relationship between andropause and liver health in American males. This article presents a detailed analysis of a 20-year study that explores the effects of hormonal changes on hepatic function, offering insights into the implications for men's health.
Study Design and Methodology
The study followed a cohort of 1,200 American males aged 40 to 70 over a 20-year period. Participants were selected based on their testosterone levels, with half of the cohort exhibiting normal levels and the other half showing signs of andropause. Regular assessments of liver function were conducted through blood tests measuring liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Additionally, liver ultrasounds were performed biennially to monitor for any structural changes.
Findings on Liver Enzyme Levels
Over the course of the study, significant differences in liver enzyme levels were observed between the two groups. Men experiencing andropause showed a consistent increase in ALT and AST levels compared to those with normal testosterone levels. By the end of the 20-year period, the andropausal group had an average ALT level 25% higher and an AST level 20% higher than the control group. These findings suggest that declining testosterone levels may contribute to hepatic stress and potential liver damage.
Ultrasound Results and Liver Structure
Ultrasound examinations revealed that men in the andropausal group were more likely to develop fatty liver disease. At the 20-year mark, 35% of the andropausal group had ultrasound evidence of fatty liver, compared to only 18% in the control group. This increased prevalence of fatty liver disease in men with low testosterone levels indicates a possible link between andropause and hepatic lipid accumulation, which can lead to more severe liver conditions if left unchecked.
Hormonal Influence on Liver Health
The study also investigated the potential mechanisms through which testosterone affects liver health. It was found that testosterone plays a role in regulating lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity, both of which are crucial for maintaining liver function. Lower testosterone levels were associated with increased insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, contributing to the development of fatty liver disease. These findings underscore the importance of hormonal balance in preserving hepatic health.
Clinical Implications and Recommendations
The results of this 20-year study have significant implications for the clinical management of andropause in American males. Healthcare providers should consider routine liver function tests for men experiencing symptoms of andropause, such as decreased libido, fatigue, and mood changes. Early detection of liver enzyme elevations and fatty liver disease can lead to timely interventions, including lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, testosterone replacement therapy.
Lifestyle Interventions and Future Research
Lifestyle interventions, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management, were shown to mitigate the negative effects of andropause on liver health. Participants who adhered to these recommendations experienced smaller increases in liver enzyme levels and a lower incidence of fatty liver disease. Future research should focus on the long-term benefits of these interventions and explore the role of other hormones in liver health during andropause.
Conclusion
This comprehensive 20-year study provides compelling evidence of the impact of andropause on liver health in American males. The findings highlight the need for increased awareness and proactive management of liver function in men experiencing hormonal changes. By understanding the relationship between testosterone and hepatic health, healthcare providers can better support their patients in maintaining overall well-being during the aging process.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- 0001) Understanding Andropause: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- 0002) Andropause: Debunking Myths and Understanding Realities for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- 0003) Andropause and Prostate Health: Navigating the Complex Link for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0004) Exploring Supplements for Andropause: Efficacy, Safety, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0005) Managing Andropause: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0006) Andropause and Cognitive Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Mental Sharpness [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0007) Andropause Management: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Aging Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0008) Navigating Andropause: Emotional Well-being and Support for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0009) Andropause in American Males: Symptoms, Diabetes Risk, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0010) Andropause: Navigating Social Impacts and Support for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0011) Andropause Effects on Skin: Essential Skincare Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0012) Andropause: Understanding Symptoms and Embracing Growth in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0013) Navigating Andropause: Emotional Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0014) Andropause: Mental Health Professionals' Role in Managing Male Menopause Symptoms [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0015) Andropause Effects on Joint Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0016) Andropause in American Men: Benefits and Risks of Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0017) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Managing Its Effects [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0018) Andropause and Depression in American Men: Symptoms, Links, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0019) Managing Andropause: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0020) Andropause: Impact on American Men's Self-Esteem and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0021) Andropause: Understanding Symptoms, Family Support, and Healthy Lifestyle Changes for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0022) Andropause and Hair Loss: Understanding Causes and Exploring Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0023) Andropause: Navigating Male Menopause with Essential Support Networks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0024) Andropause: Understanding and Managing Male Menopause in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0025) Managing Andropause: Combating Fatigue with Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0026) Andropause and Immune Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Well-being [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0027) Andropause and Digestive Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0028) Andropause and Memory: Strategies for American Males to Enhance Cognitive Function [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0029) Andropause: Managing Muscle Loss in American Males Through Exercise and Nutrition [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0030) Andropause and Cholesterol Management in American Males: Diet, Exercise, and Medical Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0031) Andropause: Managing Symptoms and Work Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0032) Andropause and Vision: Managing Eye Health in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0033) Navigating Andropause: Essential Nutrition for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0034) Hydration's Crucial Role in Managing Andropause Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0035) Andropause and Kidney Health: Understanding the Link and Managing Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0036) Andropause and Energy: Understanding and Managing Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0037) Andropause and Thyroid Function: Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0038) Andropause and Dental Health: Tips for American Males to Maintain Oral Hygiene [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0039) Andropause Impact on Liver Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0040) Mindfulness: A Key Strategy for Managing Andropause Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0041) Andropause and Blood Pressure: Monitoring and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0042) Community Support Enhances American Men's Andropause Management and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0043) Andropause in American Males: Symptoms, Stress Management, and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0044) Andropause Management: The Vital Role of Sleep for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0045) Andropause: Understanding Declining Testosterone's Impact on American Men's Motivation and Drive [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0046) Andropause and Respiratory Health: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0047) Andropause: Managing Mental Health with Essential Mental Health Days for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0048) Andropause Management: Exercise Benefits for American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0049) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Impact on American Men's Confidence [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0050) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Essential Health Screenings for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0051) Andropause and Emotional Intelligence: Enhancing Men's Well-being [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0052) Andropause and Hearing Loss: Understanding the Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- 0053) Andropause Management: The Therapeutic Role of Hobbies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- 0054) Andropause and Creativity: Managing Decline in American Men's Cognitive Output [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- 0055) Andropause and Allergies: Managing Symptoms for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- 0056) Managing Andropause: Goal Setting for American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- 0057) Andropause and Skin Sensitivity: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- 0058) Andropause: Understanding Its Impact on American Men's Purpose and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0059) Andropause and Foot Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Mobility and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- 0060) Andropause: Managing Symptoms with Time Management and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- 0061) Technology Revolutionizes Andropause Management for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0062) Andropause: Navigating Declining Testosterone and Maintaining an Adventurous Life [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0063) Andropause Impact on Nail Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0064) Volunteering: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause Symptoms in Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0065) Andropause Impact on Eye Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0066) Andropause: Managing Its Impact on Hand Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0067) Andropause and Lifelong Learning: Empowering American Men's Health Journey [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0068) Travel as Therapy: Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- 0069) Andropause and Ear Health: Protecting Hearing in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0070) Andropause Effects on Oral Health: Managing Tongue and Saliva Changes in Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0071) Andropause in American Males: Understanding Its Impact on Nose Health [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- 0072) Music Therapy: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0073) Andropause Management: Harnessing Art for Psychological and Cognitive Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0074) Andropause Impact on Throat Health: Symptoms and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0075) Andropause: Financial Planning Strategies for American Men's Health and Retirement [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0076) Andropause: Impact on American Men's Humor and Cultural Identity [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0077) Andropause: Navigating Identity and Masculinity in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0078) Andropause in American Men: Enhancing Life with Social Connections [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- 0079) Understanding Andropause: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- 0080) Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Impact on Belonging in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]