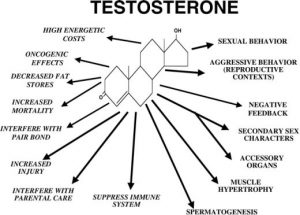
The many benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
 Reading Time: 8 minutes It’s a fact. Men’s testosterone levels are plummeting. Countless studies have found that men’s testosterone levels have been declining for decades. A 2007 study that appeared in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism concluded that there has been a “substantial drop” in men’s testosterone levels since the 1980s with the average levels diminishing by about 1% annually. What this means is that a 60-year-old man in 2004 had testosterone levels an astonishing 17% lower than a 60-year-old man did in 1987. A similar study in Denmark uncovered comparable results. In that study, Danish men born in the 1960s had...
Reading Time: 8 minutes It’s a fact. Men’s testosterone levels are plummeting. Countless studies have found that men’s testosterone levels have been declining for decades. A 2007 study that appeared in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism concluded that there has been a “substantial drop” in men’s testosterone levels since the 1980s with the average levels diminishing by about 1% annually. What this means is that a 60-year-old man in 2004 had testosterone levels an astonishing 17% lower than a 60-year-old man did in 1987. A similar study in Denmark uncovered comparable results. In that study, Danish men born in the 1960s had...